Author: Artem Timoshenko
The first half of 2024 was marked by 13th and 14th packages of sanctions. This overview unfolds new restrictions and secondary sanctions that affect Kazakhstan entities.
Sanctions on Third-Country Entities
The 13th and 14th packages introduce stringent measures targeting third-country entities that may facilitate the circumvention of sanctions. The expanded scope includes entities outside Russia in an attempt to dismantle networks that indirectly support Russia’s activities. This approach underscores the EU’s commitment to a comprehensive and effective sanctions regime.
Sanctions on Third-Country Entities
Targeting Circumvention Networks
The sanctions specifically target entities in third countries, including Kazakhstan, China, and India, which have been identified as key players in networks that circumvent existing trade restrictions. These countries are now subject to the same stringent measures as Russian companies.
The EU has identified and listed several entities (below) involved in the illicit transfer of goods and technologies to Russia. The entities have been proved to act as intermediaries, enabling the flow of dual-use items and other critical materials.
Sanctioning third-country entities, the EU aims to disrupt supply chains that allow Russia to acquire prohibited items and complicates Russia’s efforts to obtain essential goods through indirect channels.
Affected Entities
- Kazakhstan’s Da Group 22 company was included in the new package of sanctions of the European Union. The Astana-registered company was placed on the sanctions list on 25 June 2024. DA Group 22 has also been on the US sanctions list since February 2024. However, since May last year, DA Group 22 has not carried out import and export activities. According to public records, the company was incorporated in March 2022 and is listed as a small business.
- Elem Group LLP was added to the list by the Bureau of Industry and Security of the U.S. Department of Commerce in December 2023. The Kazakhstan-based Elem Group operates in logistics of electronic components, parts, industrial equipment, and spare parts.
- Subsidiary of VTB Bank JSC (Almaty, Kazakhstan) — Russia-related sanctions;[3]
- Belmagistralavtotrans Speditions GmbH (Germany; Sedlce, Poland; Smolensk, Russia; Pavlodar, Kazakhstan; Minsk, Belarus) — sanctions related to Russia;
- Defence Engineering LLP (Astana, Kazakhstan) — sanctions related to North Korea;
- Sber Vostok LLP (Almaty, Kazakhstan) — sanctions related to Russia;
- CBD-Technologies LLP (Petropavlovsk, Kazakhstan) — sanctions related to Russia.
- ITS-Astana LLP and Tynys JSC. The sanctions against the Kazakhstan companies are imposed for five years and involve a complete freeze of their assets in Ukraine.
- Tynys JSC is part of the structure of the national company Kazakhstan Engineering, with 100% of its shares owned by the Samruk-Kazyna sovereign wealth fund. As part of the state order, the company produces bulletproof vests, impact shields, and batons for the Ministry of Defense, National Guard, and penitentiary system. In 2022, Kazakhstani media reported that the company planned to start producing Kalashnikov rifles. It was also reported that the security forces of Russia and Belarus were procuring defence products from Kazakhstan.
- According to Azattyk, ITS-Astana LLP is the main supplier of welding equipment, components, and spare parts in Kazakhstan. Russian company ITS Energo, which is also included in the sanctions list, is part of the «Engineering and Technological Service» group of companies and describes itself as a leading manufacturer and supplier of welding and cutting materials and equipment in Russia.
Targeting Circumvention Networks
The sanctions specifically target entities in third countries, including Kazakhstan, China, and India, which have been identified as key players in networks that circumvent existing trade restrictions. These countries are now subject to the same stringent measures as Russian companies.
The EU has identified and listed several entities involved in the illicit transfer of goods and technologies to Russia. The entities have been proved to act as intermediaries, enabling the flow of dual-use items and other critical materials.
Enhanced Export Controls
The sanctions impose enhanced export controls on items destined for third countries that are suspected of re-exporting to Russia. This includes rigorous scrutiny of end-use and end-user declarations, and increased monitoring of high-risk trade routes.
Companies exporting to third countries must adhere to strict compliance obligations, including thorough documentation and verification processes to ensure that their goods are not diverted to Russia.
Legal and Financial Penalties
Entities found to be in violation of these sanctions face severe legal and financial penalties. This includes asset freezes, travel bans, and prohibitions on business transactions within the EU.
Sanctioned entities will have their assets within the EU frozen and their executives may be subject to travel bans, effectively isolating them from the European financial and business markets.
The sanctions prohibit EU companies from engaging in business transactions with listed third-country entities. This measure ensures that sanctioned entities cannot leverage EU markets to support Russia.
Enhanced Export Controls on Dual-Use Goods and Technologies
The 13th and 14th packages of EU sanctions against Russia significantly enhance export controls on dual-use goods and technologies. These measures are designed to prevent Russia from acquiring items that could be used to support military and defence capabilities. By broadening the scope of export restrictions, the EU aims to tighten the economic stranglehold on Russia and impair its ability to sustain military operations.
Expanded List of Dual-Use Goods
The sanctions extend the list of goods subject to export controls, particularly those with dual-use applications, which can serve both civilian and military purposes. These are categorised into 4 Tiers (below) and include advanced electronics, aerospace components, and other technologies crucial for modern warfare.
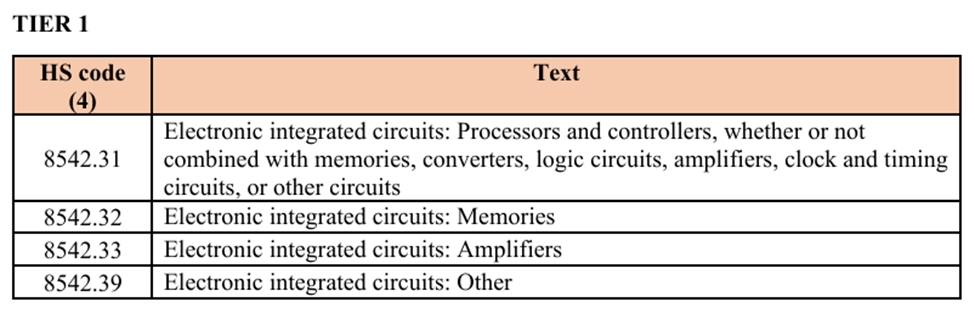
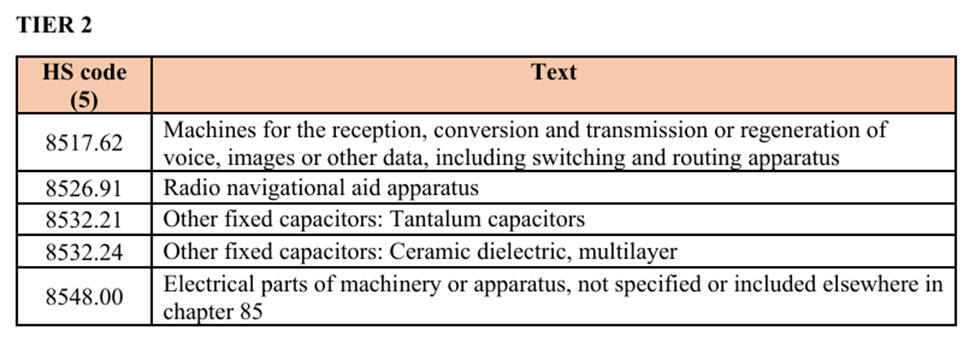


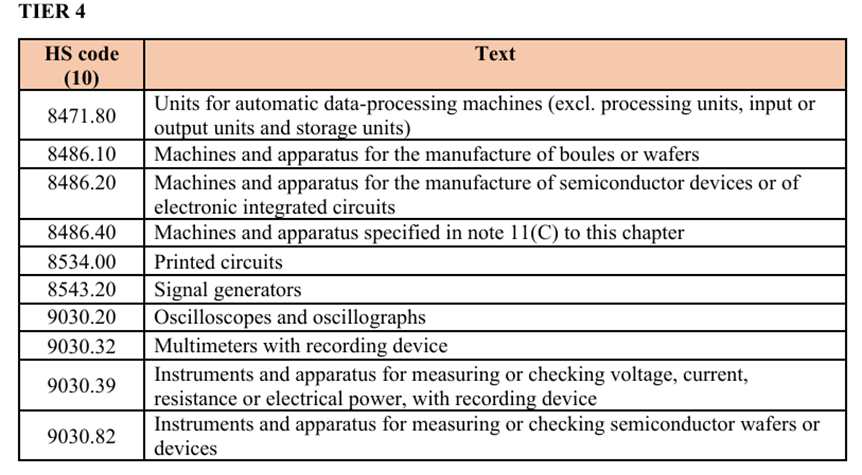
***
Unicase is a leading Central Asian law firm operating locally and internationally, with a strong presence in Kazakhstan, as well as in Uzbekistan, Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan. Unicase has one of the strongest Expert Teams, well known for regulatory and law drafting capabilities, who, alongside a strong transactional background and expertise, have allowed the firm to win major development projects and continue to be the first-choice advisers for legislation development issues.
If you would like to contact us on content and other concerning issues, please reach us at marketing@unicaselaw.com or info@unicaselaw.com.
Следите за свежими материалами, подписывайтесь здесь: Telegram, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube




